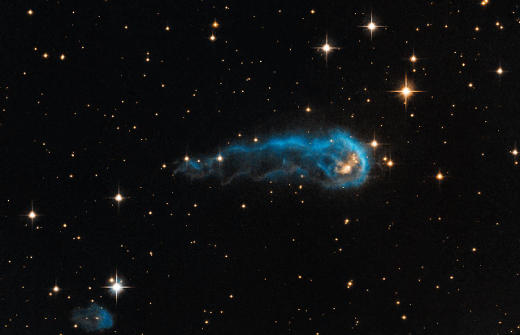
The Blue Tadpole is a clump of gas and dust, and is officially named IRAS 20324+4057. The intense blue glow seen in this Hubble picture is caused by nearby stars firing ultraviolet radiation towards it. The “head” of the tadpole contains multiple burgeoning new stars, though the glowing yellow one in this image is the largest and most luminous. Protostars eventually emerge as young stars once they have gathered enough mass from their surrounding environment. IRAS 20324+4057 as seen here is about 4,700 light years from Earth, making its way through the constellation Cygnus.