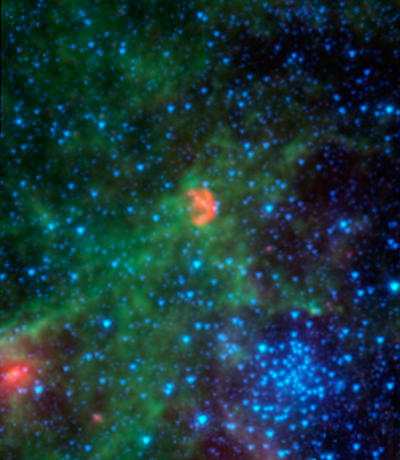
A millennium ago, about 160,000 light years away from the Milky Way galaxy, a supernova exploded in the Large Magellanic Cloud (a satellite galaxy to the Milky Way). The Spitzer space telescope’s advanced instruments picked up the infrared light emitted by dust from the remnants (red), the ambient background areas (green, yellow) and the remaining stars (blue). The closely grouped set of blue stars in the lower right of the image is the cluster known as NGC 1850. Spitzer’s Infrared Array Camera (IRAC) was used to compile the data for this picture.